Hard and soft forks
What are hard and soft forks?
In the blockchain world we often hear of these things called forks, and how they are linked to updating or upgrading a blockchain, or even is some cases forming a new blockchain. The question is then what is a Fork and what is it's impact?
In this lesson I will discuss the two types of forks which are, Hard forks and Soft forks.
Soft Forks
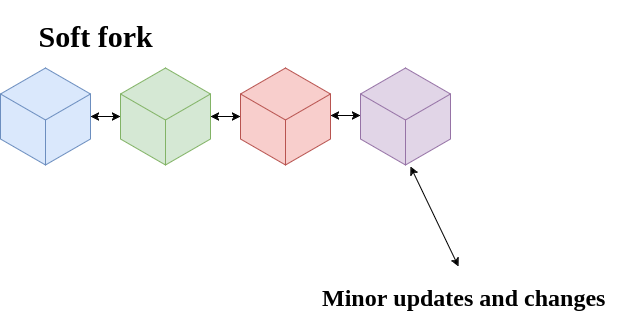
A soft fork is when the network decides they want a new feature in the blockchain. This would mean that the new version of the blockchain is fully backwards compatible. What I mean by that is, If someone opted to not update their version of the blockchain, they would still be able to use it as they were before the soft fork, and they would still be able to interact and communicate with the people on the new version. The only downside for them is they wont have the new features that have been updated to the new venison of that blockchain.
Soft forks are for simple small changes that the community decides they would like to implement.
Hard Forks
A hard fork is much more complicated. A hark for is the result of the community splitting up and starting their own thing. We have seen this with Bitcoin and Bitcoin cash, Where a lot of the users in the Bitcoin blockchain wanted to change the way Bitcoin works completely, but a lot of people who were wanting to keep to the original white paper written out by Satoshi Nakamoto and disagreed with the new changes. So Bitcoin Cash was created.
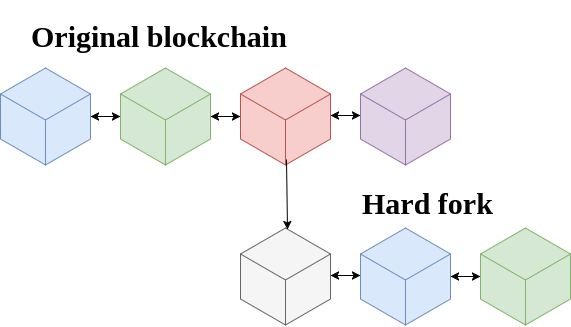
A hard fork is not backwards compatible, once it is upgraded if you havent updated to the new version you will no longer be able to interact or communicate with the people on the new fork, since a hark fork is in-fact creating a new blockchain.
Hard forks are risky because if not enough people move to the new updated version it will become useless and unusable. For this reason a lot of preparation goes into a hard fork set up. Generally people will be given a time frame until the new fork is updated. This is usually set by a block number, Saying the hard fork will happen at block number 50000 for example. At this point, anyone is able to download the new version of the blockchain, however until the hard fork time actually takes place the blockchain will look and function exactly the same as the original fork. The reason for this is to give people time to download the new blockchain and get ready for the hard fork.
Because the new fork is based on the original, all previous transactions are the same on both blocks, in the example of Bitcoin and Bitcoin cash, this means that, if you had 500 Bitcoin when Bitcoin Cash was created you would receive 500 Bitcoin cash. Because in the ledger it says you have that amount seeing that the blockchains run off of the same history. However from that point on you can no longer send or receive coins from either side of the fork.
Summary
Soft forks are for minor updates that the community agree upon, A hard fork is creating a new blockchain from the bases of the original blockchain, because there were enough people who wanted to change the way that particular blockchain worked. Because it is risky to do so and not to mention a lot of work, Hard forks arent very popular in this space. However they do happen and when they do it is always interesting to see what will come out of the fork.